Civo
This guide will show you how to install Okteto onto Civo's Kubernetes Service.
Requirements
In order to fully install Okteto, you'll need the following:
- A subdomain to which you can add a wildcard DNS record
- A Kubernetes cluster
- A working installation of kubectl
- A working installation of Helm v3 (v3.8 or higher)
- A GitHub OAuth application
- An Okteto License (optional)
Subdomain
You'll need access to a subdomain to which you can add a wildcard DNS record, such as dev.example.com.
This guide will assume that your domain is registered in Civo. Other DNS services can be used, but aren't covered here.
In the rest of this guide, we will refer to this subdomain as DOMAIN.
Deploy a Kubernetes cluster
If you are not familiar with this step, we recommend that you follow Civos's cluster creation guide.
To get started with Okteto, we recommend that you create a Kubernetes cluster with the following configuration:
- 3 large nodes
- Default network
- Without Traefik (you'll need to remove it from the default apps)
Okteto will create persistent volumes for the build and registry services, so you might need to increase your storage quotas.
Our installation guides assume Okteto will be running in a dedicated cluster. We recommend contacting our team if you plan on installing Okteto in a cluster with other workloads.
Installing kubectl
Follow the official documentation for installing kubectl. Once installed, configure kubectl to talk to your new cluster.
Installing Helm v3 (v3.8 or higher)
Follow the official documentation for installing the latest release of Helm v3 (v3.8 or higher).
Creating the GitHub OAuth application
Okteto supports OAuth providers like Google, GitHub, or OpenID Connect to handle user authentication. For this guide, we'll focus on using GitHub. All the supported configuration settings are described here.
If you are planning on using the GitHub Integration, you should follow this guide. You'll then use the same Github Application for the Integration as the one from Oauth.
Follow GitHub's official documentation on how to create an OAuth App.
When creating the OAuth App, you will need to provide the following values:
Homepage URL:
https://okteto.DOMAIN
Authorization callback URL:
https://okteto.DOMAIN/auth/callback
You'll use the Client ID and Client Secret when installing Okteto.
Getting your Okteto License
Okteto is free for up to 3 users without a license. You can also sign on for the free trial to give access up to 100 users for a month.
Installing Okteto
Create the Okteto Namespace
Run the following command to create a namespace to install Okteto in:
$ kubectl create namespace okteto
Configuring your Okteto instance
Download a copy of the Okteto Civo configuration file, open it, and update the following values:
- Your
email - Your
license(optional) - A
subdomain clientIdandclientSecretof the GitHub OAuth Application you created- You GitHub
organization. An emptyorganizationfield permits any user to log in.
For example:
email: admin@example.com
license: 1234567890ABCD==
subdomain: dev.example.com
auth:
github:
enabled: true
clientId: ae8924d074d8c8809999
clientSecret: ABCD90598b706d5342f07cce18fee5e5da391234
organization: my-org
cloud:
provider:
civo:
enabled: true
registry:
storage:
filesystem:
enabled: true
persistence:
size: 100Gi
Adding the Okteto Helm repository
You'll need to add the Okteto repository in order to be able to install Okteto:
helm repo add okteto https://charts.okteto.com
helm repo update
Installing your Okteto instance
Install the latest version of Okteto by running:
helm install okteto okteto/okteto -f config.yaml --namespace=okteto
After a few seconds, all the resources will be created. The output will look something like this:
Release "okteto" has been installed. Happy Helming!
NAME: okteto
LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Mar 26 18:07:55 2020
NAMESPACE: okteto
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
1. Create the following DNS record, pointing it to the NGINX controller service External-IP:
- "*.dev.example.com"
You can retrieve the External IP by running:
kubectl get service -l=app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx,app.kubernetes.io/component=controller --namespace=okteto
2. Once you create both DNS entries you can access your Okteto instance at this URL:
https://okteto.dev.example.com
Retrieve the Ingress Controller IP address
You can use kubectl to fetch the address that has been dynamically allocated by Civo to the NGINX Ingress you've just installed and configured as a part of Okteto:
kubectl get service -l=app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx,app.kubernetes.io/component=controller --namespace=okteto
The output will look something like this:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
okteto-ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.245.147.23 91.211.154.196 80:30087/TCP,443:31799/TCP,1234:31412/TC 2m
You'll need to create a wildcard DNS record for this IP. To do that, log in to your Civo account, click on the "Manage" option on the left part of the dashboard, and click on "DNS".
Select the domain you're using for your Okteto instance, and click on the "DNS Records" option.
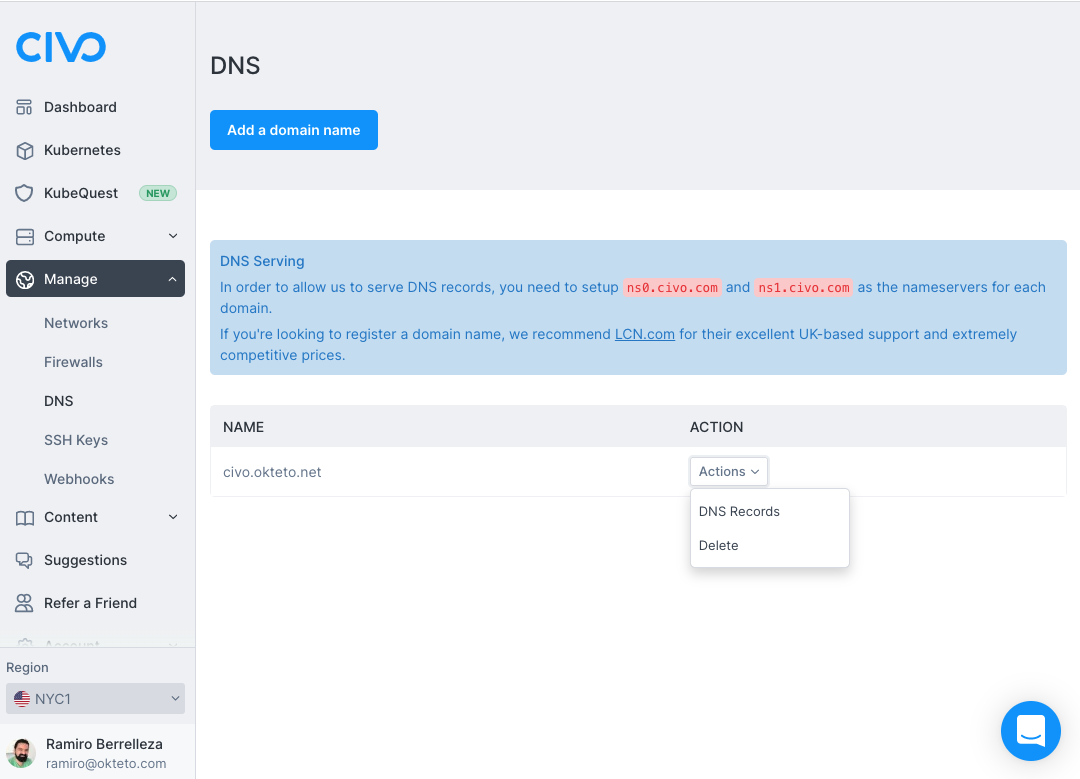
Click on the "Add a Record" button and use the following values:
- Type: A
- Name: *
- Value: Your EXTERNAL-IP
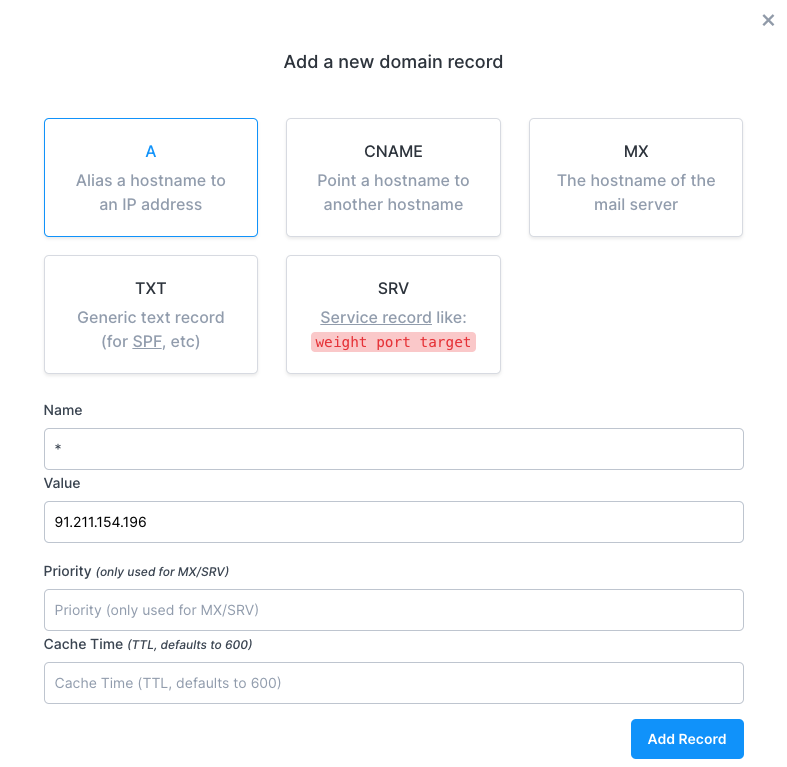
Click on the "Add Record" button to create the DNS record.
Sign in to your Okteto instance
Important: The default installation uses self-signed certificates. We strongly recommend that you configure Okteto to bring your own certificates before giving your team access to your instance.
You can access your Okteto instance at https://okteto.SUBDOMAIN. Your account will be automatically created as part of the login process. The first user to successfully log into the instance will be automatically assigned the administrator role.